I. Introduction: The Invisible Threat of Atmospheric Ozone
The Silent Killer of Polymers
Ozone is naturally present in the atmosphere, but in material science and industrial manufacturing, it is regarded as one of the most aggressive agents responsible for polymer degradation. Many polymers and elastomers contain unsaturated chemical bonds that are highly vulnerable to ozone attack. When ozone comes into contact with these materials, it reacts directly with the polymer chains, initiating a process known as ozone-induced degradation or ozone cracking. This phenomenon is particularly critical in applications where rubber components are exposed to air over long periods, making the use of an ozone test chamber essential for durability evaluation.
At the molecular level, ozone attacks the carbon–carbon double bonds present in elastomeric materials. This reaction breaks the polymer chains and reduces their ability to stretch and recover. As a result, the material gradually loses elasticity, flexibility, and mechanical strength. Even though the chemical reaction begins immediately upon exposure, the physical signs of damage are not visible at the initial stage, making ozone cracking a silent and often underestimated failure mechanism in industrial environments.
Ozone damage typically begins at the surface of the material because ozone can only react where it has direct contact with air. Fine cracks form on exposed surfaces, edges, and corners, especially in components that are under constant or intermittent mechanical stress. When the material is stretched or held under tension, the cracks tend to align perpendicular to the direction of stress. Over time, these cracks grow deeper into the material, ultimately leading to sudden and catastrophic failure without significant prior warning.
One of the most concerning aspects of ozone cracking is that it occurs even at extremely low ozone concentrations. Levels as low as a few parts per hundred million (pphm) are sufficient to initiate degradation. Since ozone exposure is cumulative, continuous low-level exposure over long periods can cause severe damage. This means that there is effectively no safe ozone threshold for many commonly used elastomers in industrial environments where long-term reliability is required.
To mitigate ozone-induced degradation, industries adopt multiple preventive strategies. These include selecting ozone-resistant materials, incorporating anti-ozonant additives into rubber formulations, applying protective surface coatings, and ensuring proper storage away from ozone sources. Additionally, accelerated ozone resistance testing using an ozone test chamber is widely used to simulate long-term exposure and predict material performance. Such testing plays a crucial role in quality assurance and is often required to meet international standards such as ASTM, ISO, and IEC.
Ozone is present naturally in the atmosphere and is often associated with environmental discussions. However, in the world of material science and industrial manufacturing, ozone is considered one of the most aggressive and destructive agents for polymers and elastomers, especially in applications involving rubber components.
Ozone-induced degradation, commonly known as ozone cracking, occurs when ozone molecules attack rubber and elastomeric materials. This damage is usually invisible at first. Over time, fine surface cracks appear, especially when the material is under tension. These cracks grow deeper and eventually lead to sudden and catastrophic failure, highlighting the importance of controlled ozone testing for material longevity.

OUR CLIENT INFO
Cosmo Analytical Lab (LLP) is a material testing and analytical services firm established in 2014 in Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India. The company operates a state-of-the-art laboratory that offers a wide range of testing and inspection services to support quality assurance, product development, and compliance with national and international standards across multiple industries.
Its services include rubber and polymer testing, metallurgical and mechanical testing, soil and rock analysis, paints and enamels testing, water and waste analysis, failure analysis, and non-destructive testing. All tests are performed using advanced instruments such as spectrometers, mechanical strength testers, humidity chambers, and other precision equipment, and are supported by a highly trained team of scientists and technicians to ensure accuracy, reliability, and timely reporting.
The lab also provides sample preparation services that help maintain consistency and quality in analytical results. Over the years, Cosmo Analytical Lab has built a reputation for precise testing, transparent reporting, and dependable customer service for businesses in construction, manufacturing, infrastructure, and environmental testing fields.

The Science of Degradation: Why Ozone Testing Is Non-Negotiable
Ozone (O₃) is a highly unstable and reactive form of oxygen. Because of this high reactivity, it readily attacks elastomers that contain unsaturated carbon–carbon double bonds in their molecular structure. These double bonds are common in many rubber materials and are essential for flexibility. When ozone comes into contact with such materials, a chemical reaction known as ozonolysis takes place, which is the root cause of ozone-induced degradation and ozone cracking evaluated using an ozone test chamber.
During ozonolysis, ozone molecules react directly with the double bonds in the polymer chains. This reaction splits the long molecular chains into shorter segments. As the polymer chains break, the material loses its ability to stretch and return to its original shape. This reduction in molecular length is directly responsible for the loss of elasticity and resilience in the elastomer under ozone exposure conditions.
- As ozone exposure continues, the surface of the material gradually becomes brittle.
- This process is referred to as surface embrittlement.
- The outer layer of the material hardens and loses its flexibility.
- The inner core of the material may still remain relatively elastic.
- This difference in mechanical properties between the hardened surface and the flexible core creates internal stress.
- The resulting internal stress makes the surface highly vulnerable to ozone-induced cracking.
Crack initiation begins at microscopic levels and is usually not visible to the naked eye in the early stages of degradation. These micro-cracks form at points where the polymer chains have been weakened the most. Once cracks appear, they act as stress concentrators. Any applied load, stretching, or vibration causes stress to focus at the crack tips rather than being evenly distributed across the material structure.
As stress concentration increases, crack growth accelerates rapidly. This explains why ozone-related material failures often seem sudden and unexpected in real-world applications. A component may function normally for a long time, but once cracks reach a critical depth, failure occurs abruptly. This delayed but catastrophic failure pattern makes ozone attack particularly dangerous in industrial applications where reliability and safety are critical.
In practical terms, this chemical mechanism highlights why ozone resistance is a key material selection criterion. Understanding ozonolysis helps engineers design better products, choose appropriate elastomers, and implement preventive measures such as stress reduction, material protection, and accelerated ozone testing using an ozone test chamber to predict real-world material performance.

Environmental Variables That Accelerate Cracking
Ozone-induced cracking is strongly influenced by surrounding environmental conditions and rarely occurs as a standalone phenomenon. In real industrial settings, multiple environmental variables act together to accelerate the degradation process. Among these, temperature and humidity play a particularly important role in determining how quickly ozone attack progresses and how severe the resulting material damage becomes under ozone exposure.
Temperature has a direct impact on the speed of chemical reactions between ozone and elastomeric materials. As temperature increases, ozone molecules become more reactive, and the rate of ozonolysis rises significantly. Elevated heat also weakens polymer chains, reducing their resistance to chemical attack. This combination leads to faster loss of elasticity, quicker surface embrittlement, and earlier crack formation compared to materials exposed to lower temperature conditions.
Humidity also affects ozone-related degradation, mainly through its influence on surface chemistry. Moisture present in the air can change how ozone interacts with the polymer surface, sometimes intensifying surface reactions. High humidity levels may lead to more irregular and deeper cracking patterns, especially when combined with mechanical stress. In certain elastomers, moisture can further soften the surface, making it more vulnerable to ozone-induced damage.
Because industrial environments rarely involve a single variable in isolation, materials are often exposed simultaneously to ozone, heat, humidity, and mechanical stress. This complex interaction makes it difficult to predict real-life performance using field observation alone. As a result, controlled laboratory ozone testing using an ozone test chamber becomes essential. Such testing allows manufacturers to simulate combined environmental conditions in a controlled manner, evaluate material durability, and ensure reliable performance before products are deployed in real-world applications.
Application of the Ozone Test Chamber
An ozone test chamber that combines ozone concentration, temperature, and humidity control is used to evaluate how materials perform under aggressive, real-world environmental conditions. Its applications span multiple industries where the long-term reliability of polymers and elastomers is critical to safety and performance.
In the automotive industry, ozone test chambers are used to test rubber hoses, seals, gaskets, belts, and tire components. These parts are continuously exposed to heat, humidity, and ozone generated by engines and electrical systems. Ozone testing helps manufacturers predict cracking, loss of elasticity, and service life before the components are installed in vehicles.
In electrical and power equipment applications, the ozone test chamber is used to evaluate insulating materials, cable sheathing, bushings, and rubber seals used in substations and switchgear. Ozone generated by electrical arcing and corona discharge can severely damage insulation over time. Temperature and humidity control in the chamber helps simulate actual operating conditions and ensures long-term electrical safety.
In aerospace and defense applications, ozone test chambers are used for testing elastomeric seals, O-rings, fuel system components, and vibration-isolating materials. These components must withstand extreme temperature variations, controlled humidity, and ozone exposure at high altitudes. Accelerated ozone testing ensures compliance with strict reliability and safety standards.
In the medical and healthcare industry, ozone test chambers are applied to evaluate rubber and polymer components used in medical devices, tubing, seals, and protective equipment. Since many healthcare environments use ozone or ozone-based sterilization systems, testing under controlled humidity and temperature ensures material stability, safety, and regulatory compliance.
In water and wastewater treatment plants, ozone test chambers are used to assess the durability of seals, membranes, gaskets, and coatings exposed to ozone-based disinfection systems. The combined effect of high humidity, ozone, and varying temperatures closely represents real plant conditions, helping operators avoid unexpected material failures.
In the rubber and polymer manufacturing industry, ozone test chambers are widely used for material research, formulation development, and quality control. Manufacturers test different rubber compounds, additives, and protective coatings to compare ozone resistance under controlled environmental stress and optimize product performance.
In consumer goods and industrial equipment, ozone test chambers are used to test rubber parts in appliances, HVAC systems, industrial machinery, and packaging materials. Temperature and humidity control allow realistic simulation of storage and operating environments, ensuring product durability throughout its lifecycle.
Overall, an ozone test chamber with integrated humidity and temperature control is essential for accelerated aging studies, material comparison, failure analysis, and standards compliance. It enables manufacturers to simulate harsh environmental conditions in a short time, reduce field failures, and deliver reliable, long-lasting.

Advantages of the Ozone Test Chamber
One of the major advantages of using an ozone test chamber is its ability to predict long-term material performance within a short period. In actual service environments, ozone-related damage may take several months or even years to become visible. An ozone test chamber accelerates this natural aging process by exposing materials to controlled ozone concentration, temperature, and humidity. This controlled acceleration allows manufacturers to evaluate how materials will behave throughout their complete service life without waiting for real-time degradation.
Another important benefit is the early detection of ozone-induced cracking and material degradation. Ozone damage generally starts at the surface level and remains invisible during the initial stages. The ozone test chamber helps identify early signs such as micro-cracks, surface embrittlement, and gradual loss of elasticity before complete structural failure occurs. This early identification enables manufacturers to take corrective actions such as improving material formulation, modifying design, or replacing unsuitable materials.
The ozone test chamber also provides a highly controlled and repeatable testing environment. Unlike outdoor or field exposure, laboratory testing ensures stable and consistent ozone concentration, temperature, and humidity throughout the entire test cycle. This repeatability allows accurate comparison between different materials, rubber compounds, and production batches, ensuring that test results are reliable and scientifically valid.
Accurate simulation of real-world environmental conditions is another key advantage. Many industrial applications involve combined exposure to ozone, heat, and moisture. An ozone test chamber is designed to replicate these combined conditions in a controlled laboratory setting, making the test results more realistic and meaningful for actual operating environments.
Improved selection of ozone-resistant materials is a direct outcome of ozone testing. By comparing the ozone resistance of different elastomers and polymers, manufacturers can select the most suitable material for specific applications. This helps in designing products that offer better durability and longer service life in ozone-rich environments.
The use of an ozone test chamber significantly reduces the risk of sudden and unexpected product failures. Since ozone cracking often leads to catastrophic breakdown without visible warning signs, accelerated testing helps identify weak materials at an early stage, improving overall product reliability and safety.
Quality control and manufacturing consistency are also strengthened through ozone testing. Manufacturers can test samples from different production batches to ensure uniformity in material properties. This minimizes performance variations and helps maintain consistent quality standards across production runs.
Ozone test chambers support product development and material research activities as well. Engineers and researchers can evaluate new rubber formulations, additives, and protective coatings by observing their behavior under controlled ozone exposure. This accelerates innovation and improves overall product performance.
From a business perspective, ozone testing helps reduce warranty claims and long-term maintenance costs. Products that are tested and validated for ozone resistance are less likely to fail in real-world conditions, leading to fewer customer complaints and reduced replacement expenses.
Compliance with international testing standards is another critical advantage. Ozone test chambers are designed to conduct tests in accordance with ASTM, ISO, and IEC standards. This ensures regulatory compliance and enables products to be accepted in global markets.
Technical Specifications of Ozone Test Chamber
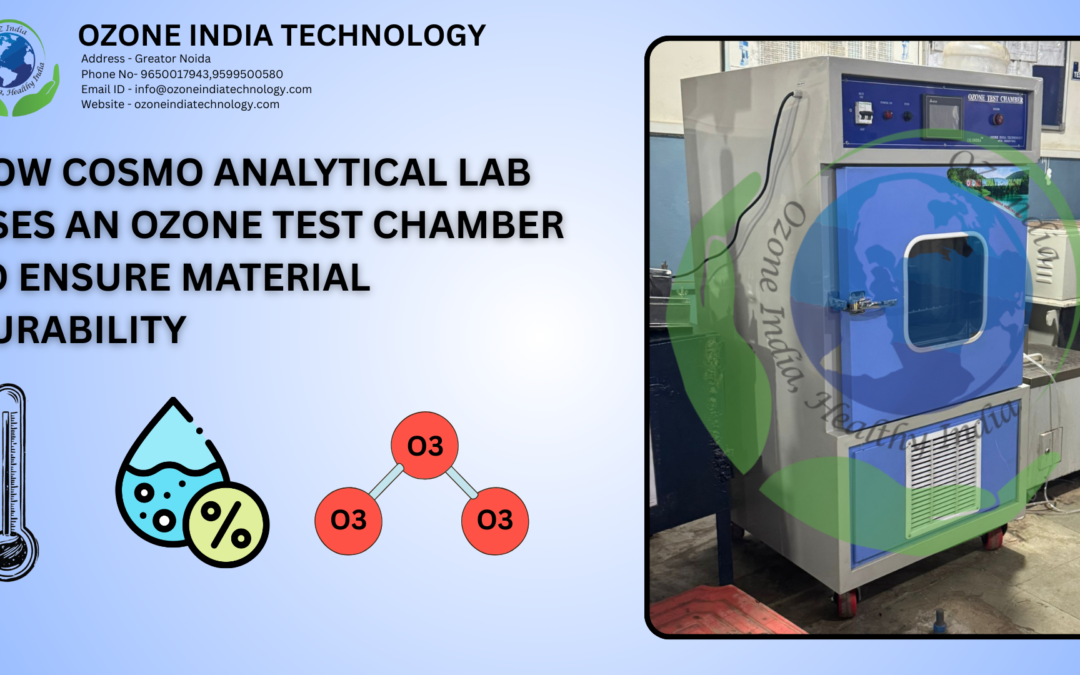
The ozone test chamber is designed to perform accelerated ozone aging and ozone cracking tests under controlled environmental conditions. The system integrates ozone generation, temperature control, humidity regulation, and uniform air circulation to ensure accurate and repeatable test results.
The cooling system of the chamber is equipped with a copper cooling coil, which provides efficient heat transfer and stable temperature control during extended testing cycles. Copper is selected for its high thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance, ensuring long-term system durability.
The sample holder is manufactured from stainless steel, offering excellent resistance to ozone, humidity, and corrosion. The holder is adjustable and allows secure positioning of test specimens under the required stress conditions as specified in international testing standards.
The ozone generation system operates on the corona discharge principle, ensuring stable and consistent ozone production. The generator uses IGBT-based corona technology, which offers high efficiency, precise control, and long operational life. The ozone electrode is constructed from stainless steel grade 316, providing superior resistance to oxidation and chemical attack.
For air supply, the chamber includes an in-built oil-free air compressor. This ensures clean and dry air input, preventing contamination and maintaining accurate ozone concentration throughout the test process.
The chamber features a digital display compatible with a microcontroller, allowing precise monitoring and control of ozone concentration, temperature, humidity, and test duration. This improves operational convenience and ensures repeatable testing conditions.
Uniform ozone distribution inside the chamber is achieved using a 4-inch circulation fan. The fan operates at selectable speeds of 2650 and 2900 RPM, delivering airflow rates of 85 and 110 CFM. It provides static pressure levels of 3.2 and 4.5 mm H₂O, ensuring consistent airflow across all test samples. The fan is designed for low-noise operation, maintaining noise levels of 43 and 48 dB(A), making it suitable for laboratory environments.
Overall, the ozone test chamber is engineered for reliable performance, long-term stability, and full compliance with international ozone testing standards, making it suitable for research laboratories, quality control departments, and industrial testing facilities.
Why Us
Our ozone test chambers are designed with a strong focus on accuracy, reliability, and real-world simulation. By integrating precise ozone generation with controlled temperature and humidity, we ensure test conditions closely replicate actual service environments. High-quality components such as stainless steel sample holders, copper cooling coils, and IGBT-based corona ozone generators deliver stable performance, long equipment life, and consistent results across repeated test cycles.
We emphasize user-friendly operation and dependable engineering. The microcontroller-compatible digital display allows easy monitoring and control of all test parameters, while uniform air circulation ensures equal ozone exposure for every sample. Each chamber is engineered to meet the practical needs of testing laboratories, research facilities, and quality control departments, minimizing downtime and maintenance requirements.
Beyond equipment, we provide technical support and application guidance to help clients achieve meaningful and standards-compliant test results. Our commitment to quality, customization, and after-sales support makes us a reliable partner for organizations seeking accurate ozone testing solutions and long-term value from their investment.

It was very informative. Let me contact u for more details
Yeah sure,
Mail us at [email protected] or contact us at +91 9318305878